Professional Security Camera Systems
A complete, plain-English guide to choosing a professional security camera system that actually performs: wired PoE IP cameras, reliable NVR recording, correct lens selection, storage sizing, installation best practices, and the key differences between pro and consumer cameras.
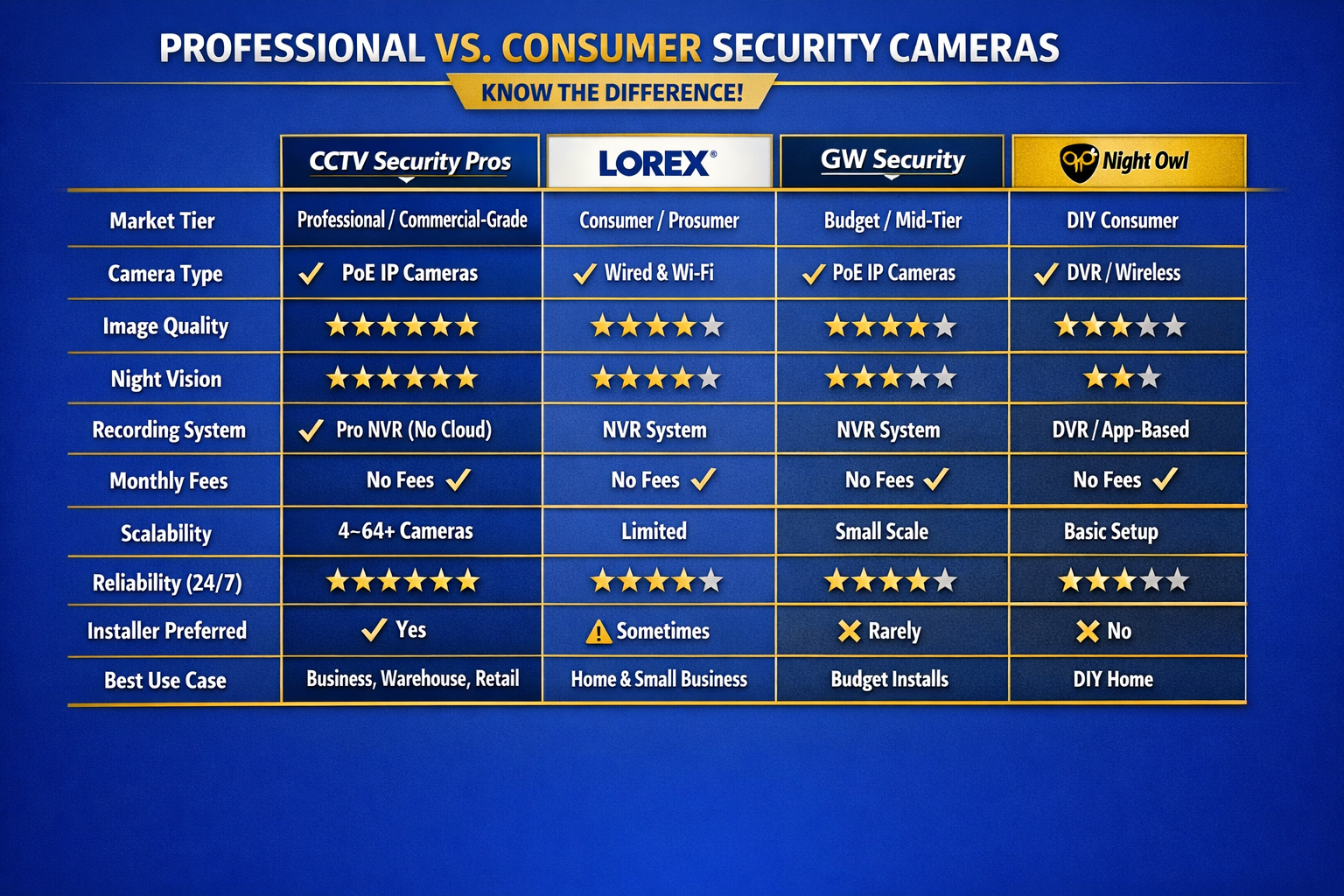
Professional vs Consumer Security Camera Systems
The biggest difference isn’t “4K vs not 4K.” It’s the architecture. Professional systems use wired PoE cameras and an on-site NVR for stable recording, real evidence, and long-term ownership. Consumer systems often rely on Wi-Fi, batteries, and app-first ecosystems—fine for casual monitoring, but not ideal for dependable 24/7 coverage.
Core Components: IP Cameras, NVR, PoE Cabling
- PoE IP Cameras: deliver high-resolution video over Ethernet and get reliable power through the same cable.
- NVR Recorder: stores your video on-site and gives you fast playback, export, and remote viewing.
- PoE Cabling: one cable per camera for power + data—stable, scalable, and installer-friendly.
Camera Types & Best Use Cases
Lens / Distance “Clarity” (Why Some 4K Footage Still Looks Useless)
Resolution matters—but lens choice and distance matter more. A wide-angle camera can be “4K” and still fail at identification if the subject is too far away. Professionals solve this with a simple strategy: wide coverage + zoom detail.
Night Vision & Lighting (Real-World Fixes)
- Avoid aiming directly into headlights or strong light sources.
- Prevent IR reflection off nearby walls/soffits for clearer night images.
- Use a varifocal camera for critical night detail zones (doors, gates, docks).
- Use dedicated LPR cameras for reliable license plate capture at night.
Storage & Retention (7 vs 14 vs 30+ Days)
Storage is sized from camera count, resolution, recording mode (24/7 vs motion), and how many days you want to keep video. Start by choosing a retention target—then size drives accordingly.
Remote Viewing & Cybersecurity (Do This Like a Pro)
- Use unique strong passwords (no defaults).
- Create admin vs viewer users (least privilege access).
- Keep firmware updated based on your environment.
- Test playback and exports before you ever “need” them.
Design & Placement (Avoid Blind Spots)
- Cover every entrance (approach + at-the-door detail).
- Overlap perimeter views so there’s no single point of failure.
- Add zoom cameras anywhere distance matters (gates, docks, driveway).
- Avoid harsh backlight (sun and headlights) when possible.
Buyer Checklist (Copy/Paste This)
- Camera count: ___ now / ___ later
- Critical zones: doors, registers, docks, gates, driveway
- Recording: 24/7 on ___ cameras, motion on ___ cameras
- Retention goal: ___ days
- Remote users: ___ viewers, ___ admins

